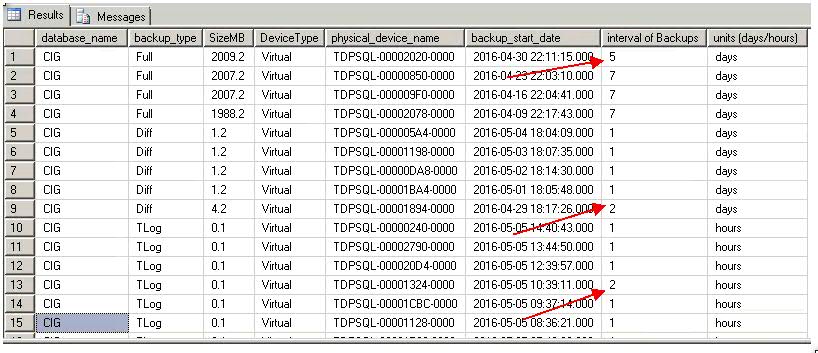
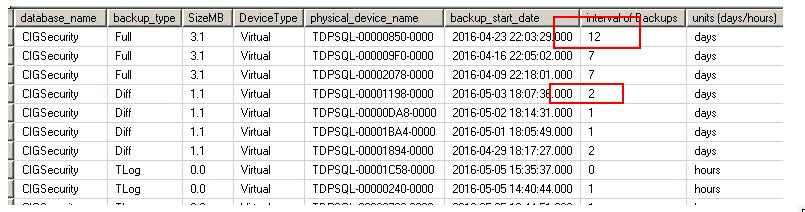
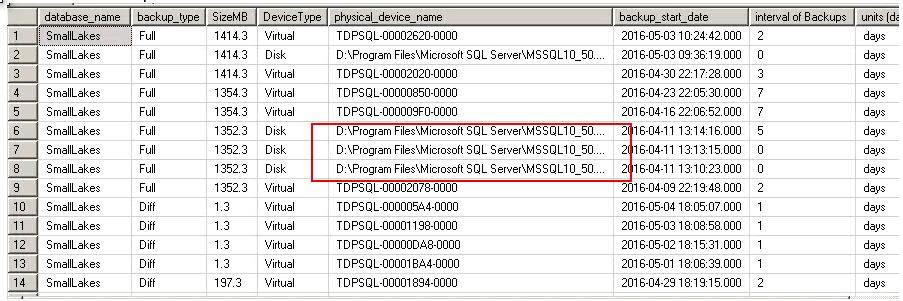
This script is taken from Thomas LaRock, and I'm shamelessly modifying it a little… just a little.
The original article is here
https://thomaslarock.com/2012/10/how-to-find-currently-running-long-sql-agent-jobs/
/*=============================================
Author: Thomas LaRock, http://thomaslarock.com/contact-me/
MODIFIED AND ADAPTED BY MIGUEL QUINTANA 01/27/2017
Summary: This script will check to see if any currently
running jobs are running long.
Variables:
@MinHistExecutions - Minimum number of job runs we want to consider
@MinAvgSecsDuration - Threshold for minimum duration we care to monitor
@HistoryStartDate - Start date for historical average
@HistoryEndDate - End date for historical average
These variables allow for us to control a couple of factors. First
we can focus on jobs that are running long enough on average for
us to be concerned with (say, 30 seconds or more). Second, we can
avoid being alerted by jobs that have run so few times that the
average and standard deviations are not quite stable yet. This script
leaves these variables at 1.0, but I would advise you alter them
upwards after testing.
Returns: One result set containing a list of jobs that
are currently running and are running longer than two standard deviations
away from their historical average. The "Min Threshold" column
represents the average plus two standard deviations.
Date: October 3rd, 2012
SQL Server Versions: SQL2005, SQL2008, SQL2008R2, SQL2012
You may alter this code for your own purposes. You may republish
altered code as long as you give due credit.
THIS CODE AND INFORMATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
=============================================*/
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE
@HistoryStartDate datetime
,@HistoryEndDate datetime
,@JOB_STATE INT = 4
-- @JOB_STATE = 4 idle, @JOB_STATE = 1 running
,@MinHistExecutions int = 10.0
,@MinAvgSecsDuration int = 600.0
SET @HistoryStartDate = DateAdd(dd,-30,GETDATE()) --'19000101'
SET @HistoryEndDate = GETDATE()
/***** DO NOT MODIFY BELOW *********/
DECLARE @RESULTS TABLE (
[job_id] [uniqueidentifier] NOT NULL,
[JobName] [sysname] NOT NULL,
[State] [varchar](29) NOT NULL,
[ExecutionDate] [datetime] NULL,
[AverageSecs] [numeric](38, 6) NULL,
[DurationSecs] [float] NULL,
[capture_time] [datetime] NOT NULL
)
DECLARE @currently_running_jobs TABLE (
job_id UNIQUEIDENTIFIER NOT NULL
,last_run_date INT NOT NULL
,last_run_time INT NOT NULL
,next_run_date INT NOT NULL
,next_run_time INT NOT NULL
,next_run_schedule_id INT NOT NULL
,requested_to_run INT NOT NULL
,request_source INT NOT NULL
,request_source_id SYSNAME NULL
,running INT NOT NULL
,current_step INT NOT NULL
,current_retry_attempt INT NOT NULL
,job_state INT NOT NULL
)
--capture details on jobs
INSERT INTO @currently_running_jobs
EXECUTE master.dbo.xp_sqlagent_enum_jobs 1,''
;WITH JobHistData AS
(
SELECT job_id
,date_executed=msdb.dbo.agent_datetime(run_date, run_time)
,secs_duration=run_duration/10000*3600
+run_duration%10000/100*60
+run_duration%100
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory
WHERE step_id = 0 --Job Outcome
AND run_status = 1 --Succeeded
)
,JobHistStats AS
(
SELECT job_id
,AvgDuration = AVG(secs_duration*1.)
,AvgPlus2StDev = AVG(secs_duration*1.) + 2*stdevp(secs_duration)
FROM JobHistData
WHERE date_executed >= DATEADD(day, DATEDIFF(day,'19000101',@HistoryStartDate),'19000101')
AND date_executed < DATEADD(day, 1 + DATEDIFF(day,'19000101',@HistoryEndDate),'19000101')
GROUP BY job_id HAVING COUNT(*) >= @MinHistExecutions
AND AVG(secs_duration*1.) >= @MinAvgSecsDuration
)
-- INSERT INTO @RESULTS
SELECT JHS.job_id
,j.name AS [JobName]
,case crj.job_state
when 0 then 'not idle or suspended'
when 1 then 'Executing'
when 2 then 'Waiting for thread'
when 3 then 'Between retries'
when 4 then 'Idle'
when 5 then 'Suspended'
when 7 then 'Performing completion actions'
else ''
end as [State]
,MAX(act.start_execution_date) AS [ExecutionDate]
,AvgDuration AS [AverageSecs]
,AvgPlus2StDev AS [DurationSecs]
,GETDATE() AS [email_Done]
FROM JobHistData jd
JOIN JobHistStats jhs on jd.job_id = jhs.job_id
JOIN msdb..sysjobs j on jd.job_id = j.job_id
JOIN @currently_running_jobs crj ON crj.job_id = jd.job_id
JOIN msdb..sysjobactivity AS act ON act.job_id = jd.job_id
AND act.stop_execution_date IS NULL
AND act.start_execution_date IS NOT NULL
WHERE 1=1
AND secs_duration > AvgPlus2StDev
AND DATEDIFF(SS, act.start_execution_date, GETDATE()) > AvgPlus2StDev
-- THIS SECTION EXCLUDE JOBS ALREADY IN THE SYSTEM FOR LESS THAN 30 MINS
AND JHS.job_id NOT IN (SELECT A.JOB_ID FROM DBA.dbo.JOBS_Running_Long A WHERE DATEDIFF(mi,A.CAPTURE_TIME,GETDATE()) < 30)
AND crj.job_state = @JOB_STATE
GROUP BY JHS.job_id, j.name, AvgDuration, AvgPlus2StDev, crj.job_state